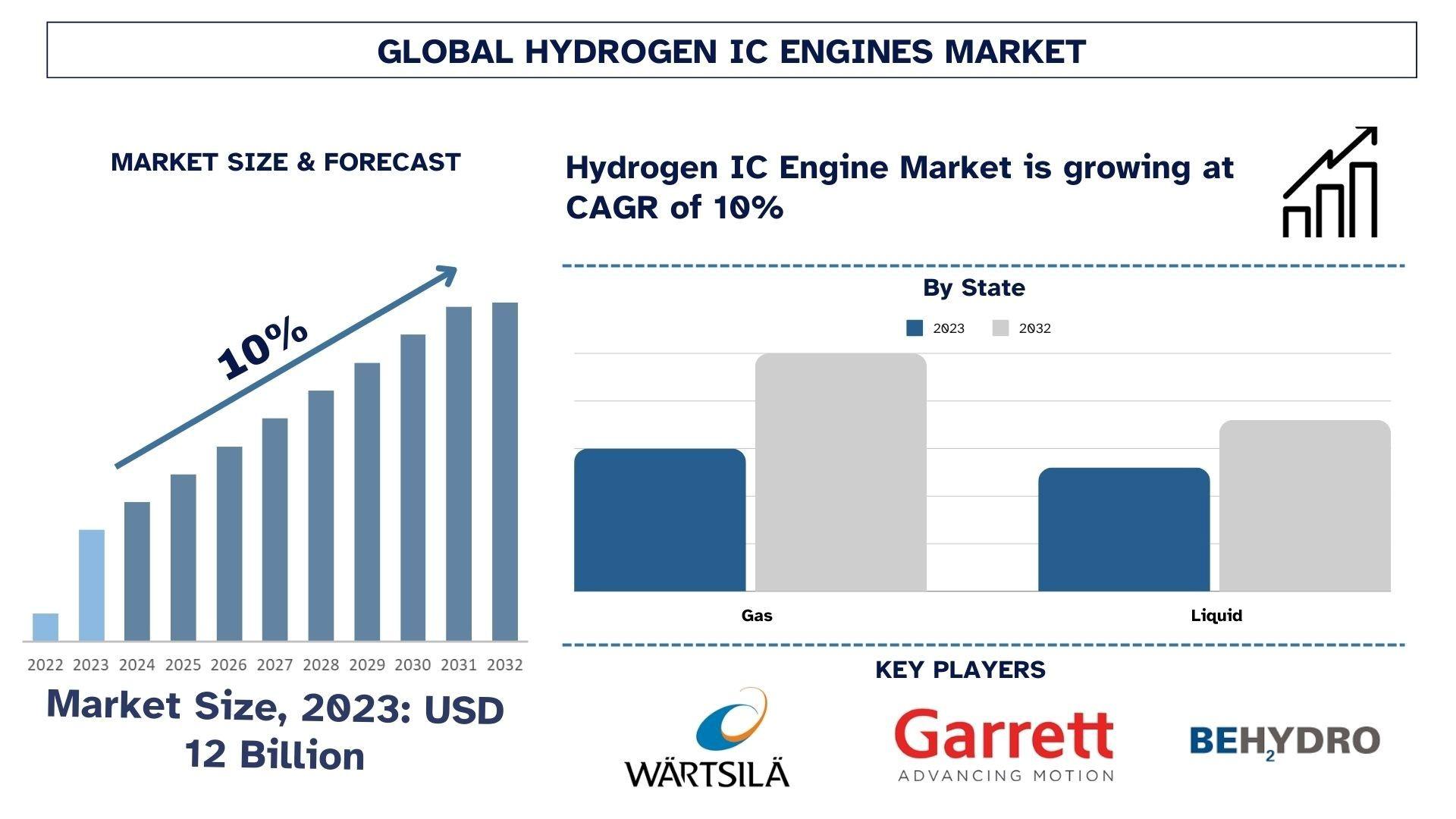
According to a new report by UnivDatos, The Hydrogen IC Engine Market was valued at approximately USD 12 Billion in 2023 and is expected to grow at a robust CAGR of around 10% during the forecast period (2024-2032).
Introduction
The Hydrogen Internal Combustion Engine (ICE) market is gradually entering a promising phase for decreasing carbon emissions in industries that heavily rely on fossil fuels. Hydrogen ICE stands for Internal Combustion Engine, it has a burning of hydrogen instead of gasoline or diesel since it has the potential to pave the way for clean energy sources, especially in industries that cannot be electrified. Although the hydrogen fuel cell has attracted most of the focus relating to hydrogen-powered motor vehicles, hydrogen ICE vehicles offer a new approach that utilizes mainstream engine systems and facilities. Given renewed attention from governments and industries of developed as well as developing nations, the hydrogen ICE market will continue experiencing advances and adding value in the future.
Access sample report (including graphs, charts, and figures): https://univdatos.com/reports/hydrogen-ic-engine-market?popup=report-enquiry
Increasing demand for a government outlook
It is noteworthy that hydrogen ICE technology is directly associated with government programs for countering climate change and decreasing carbon emissions. Emission regulators in the European Union, North America, and Asia-Pacific are setting high emission standards to reduce the impact on transport and industries. To reduce emissions to nearly zero by mid-century and beyond, hydrogen has been recognized as an important part of the energy system.
Governments are not only providing incentives through subsidies etc., to promote the use of hydrogen technology but are directly participating in the infrastructural development of hydrogen technology. EU has laid down targets regarding the penetration of hydrogen in various sectors and subsidies are being provided for developing generation, storage, and transport infrastructure for hydrogen. Similarly, nations such as Japan and South Korea have committed significant portions of their national budgets to hydrogen economies and dedicated good funds to research, development, and pilot projects. Such governmental support is driving the need for hydrogen ICEs mainly in sectors that are difficult to electrify such as heavy industries and transport mainly. Through the hydrogen option, governments strive to achieve a portfolio power mix of associated fuels and specific power, which is renewable, as ICE apps in transportation and power generation industries require.
Use of Hydrogen ICE Technology
Hydrogen ICE technology systems are quickly finding more uses, particularly in transportation and industrial power.
Transportation: The potential hydrogen ICE customers include heavy-duty vehicle segments like trucks buses and off-road machinery. In these segments, where high power and short refueling times are of paramount importance, hydrogen ICEs are again a viable competitor to battery electric vehicles, which are often hampered by their range and charge times. Furthermore, hydrogen ICEs enable the fleshing out of standard engine architectures, which makes the conversion to burn hydrogen even more convenient and cheap.
Industrial Power Generation: Further, hydrogen ICEs are also considered for industrial power generation applications in stand-alone power systems. The specified technologies are necessary in many industries, for example in mining and construction where there is often little or no access to electricity grids. While less efficient in terms of fuel conversion to electricity than diesel generators, the ICEs fed by hydrogen can provide a means for producing power with less emissions, which makes them attractive for many industries desiring to upgrade their emission-intense power units without significantly sacrificing situational versatility.
Marine and Aviation Sectors: The other industries that have also shifted focus toward hydrogen ICE technology include marine and aviation though are still in their initial stage. For instance, through hydrogen ICEs, ships and aircraft that usually require heavy fossil fuels can be run. This could bring down emissions greatly particularly in short-haul and intercoastal operations.
Hydrogen ice technology is applied in different industries and this makes it a good transitional technology to the green energy solution. Overall, as improvements in hydrogen storage delivery and engineering of ICEs start being made, so should the range of applications for hydrogen ICEs.
Cost Considerations
The biggest problem with hydrogen ICEs is the cost of producing, storing, and distributing this fuel which hampers large-scale use of the technology. Now, hydrogen is more costly to manufacture than other fossil fuels mainly because over 95% of it is generated using steam methane reforming, which is resource and energy-demanding, and it has drawbacks to the environment. Electrolysis using renewable energy sources to produce what is called ‘green hydrogen’ is cleaner, but again more expensive.
Nevertheless, hydrogen ICE also retains its cost competitiveness compared to other hydrogen-based technologies such as hydrogen fuel cells. Hydrogen ICEs can be built from current ICE manufacturing technologies with some modifications to existing manufacturing facilities. These cut the development cost and allow automakers to introduce hydrogen ICE vehicles into the market much more quickly and cheaply.
Manufacturing Hydrogen ICEs
The generation of hydrogen ICEs shares many technical similarities with traditional internal combustion engines, a factor that will benefit car makers. This is because besides using several similar technologies and infrastructure in various levels of hydrogen ICE manufacture and distribution which was earlier existing for the traditional ICEs, manufacturers of automobiles can adopt some unique features in design that will suit the best for hydrogen-powered ICEs. When applied, new production lines are not necessary to achieve the creation of hydrogen ICEs that can be made with only slight modifications to existing standard lines; this allows for less time and cost compared to the development of completely novel technologies like hydrogen fuel cells and electrical motors.
However, there are several technical changes for enhancing ICEs for hydrogen. Because hydrogen has a lower energy density than gasoline or diesel, it may be necessary to modify the engine part to achieve the same level of performance as that of gasoline or diesel engines. This also requires modification of the fuel injection system, intake and exhaust, and cooling system to accommodate for properties of hydrogen such as high level of flammability and low ignition energy.
Manufacturers are also coming up with halfway solutions using a combination of hydrogen ICEs and battery systems aimed at cutting fuel consumption. This type of system can aid in decreasing hydrogen’s energy density while still allowing for regenerative braking, and electrically assisted power in automobiles. Also, the development of a strategic alliance with suppliers and builders of hydrogen fuel is on the rise due to scale issues, where entities offer partnerships for the simultaneous seizing of demand for vehicles and fuelling infrastructure.
Click here to view the Report Description & TOC https://univdatos.com/reports/hydrogen-ic-engine-market
Conclusion
The Hydrogen Internal Combustion Engine (ICE) market is presented as a modern solution for those industries that are eager to switch to hydrogen but are still incapable of abandoning the ICE conception. The direct regulation by the governments to cut down the emission levels and promote the hydrogen infrastructure plays a key role in the development wherein transportation and industrial power sectors are of paramount importance. While serving heavy-duty vehicles, the basic building block structure of hydrogen ICEs can flexibly extend to other applications like stationary power generation and marine markets.
Thus, cost continues to be an issue; however, further investments into hydrogen production and infrastructure guarantee it gradually becomes less costly as the main solution for hydrogen ICE technology. Notably, hydrogen ICEs can be produced using existing production lines, which makes them scalable, especially for automakers seeking to transition to hydrogen without requiring them to come up with entirely new vehicle architectures.
As industries remain focused on reliable affordable clean energy technologies hydrogen ICEs perfectly hold the key. Owing to the dual requirements of performance and efficiency not to mention minimized emissions, hydrogen ICE technology will probably be decisive in the determination of the principles of mass utilization of hydrogen as a clean energy source. It’s possible now to conclude that the future of the hydrogen ICE market mainly depends on the further progress of these tendencies and the support of adequate policies and investments in the hydrogen infrastructure.
Related Report
Hydrogen Fuel Cell Electric Vehicle Market: Current Analysis and Forecast (2023-2030)
Green Hydrogen Market: Current Analysis and Forecast (2023-2030)
Hydrogen Storage System Market: Current Analysis and Forecast (2023-2030)
Alternative Fuel and Hybrid Vehicle Market: Current Analysis and Forecast (2023-2030)
Hydrogen Powered Tractor Market: Current Analysis and Forecast (2023-2030)
Contact Us:
UnivDatos
Contact Number - +1 978 733 0253
Email - [email protected]
Website - www.univdatos.com
Linkedin- https://www.linkedin.com/company/univ-datos-market-insight/mycompany/